The Speed of Light and the Future of Photonic Wire Bonding
Light, traveling at an astonishing speed of nearly 300,000 kilometers per second in a vacuum, can circumnavigate the Earth about seven and a half times in just one second. At speeds of around 200,000 kilometers per second in fiber optic materials, light trapped in an optical fiber could circle the Earth five times in that one second.
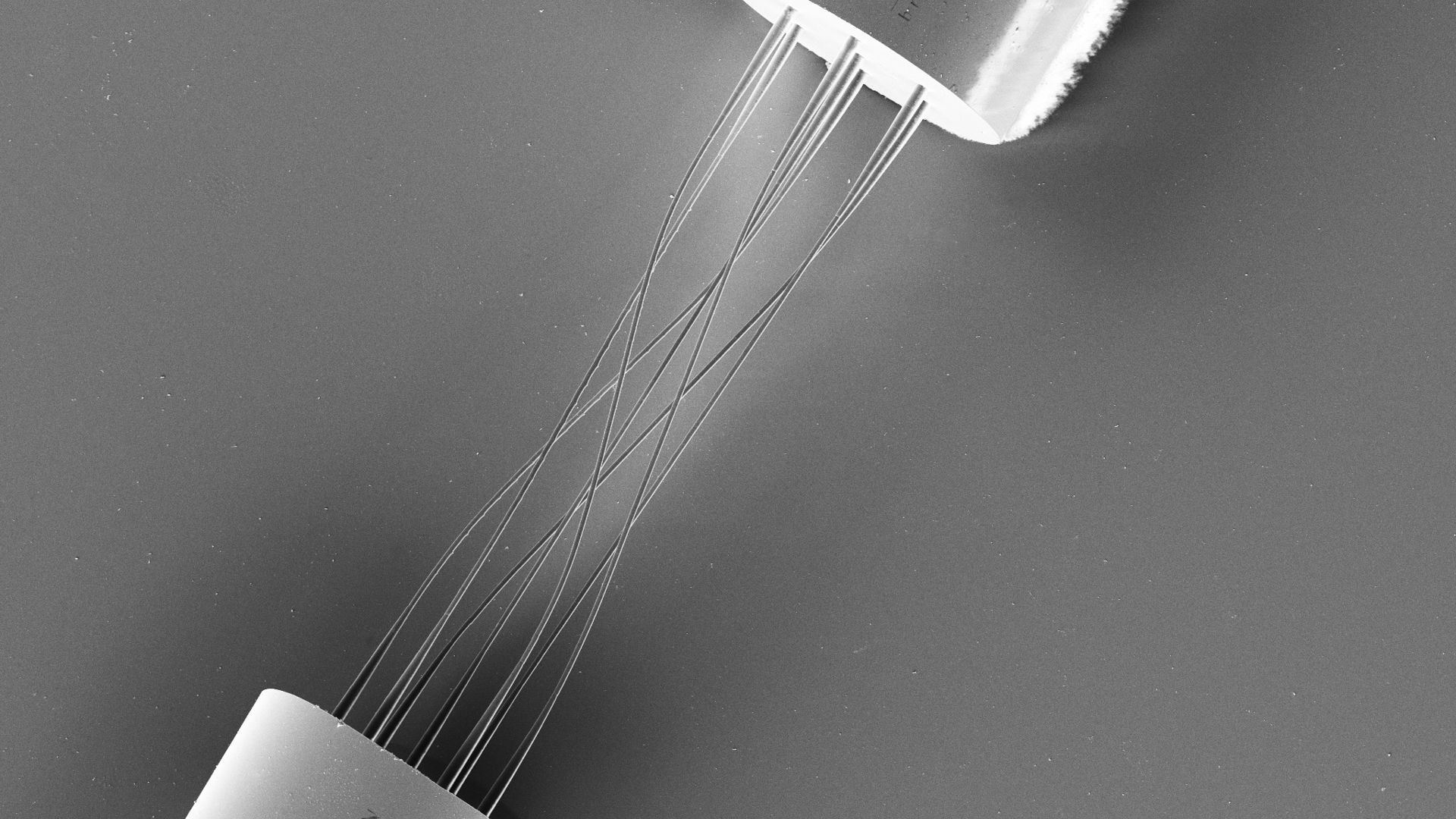
Scientific breakthroughs in engineering mean we can control the path that light travels and shape it into ultra-fast light pulses, lasting much less than one billionth of a second. This extraordinary speed and control underlies one of the most promising technologies of the future: Photonic Wire Bonding. This emerging field leverages both the precise control and the speed of light to revolutionize data transmission and enhance the efficiency of computing systems.
The Basics of Photonic Wire Bonding
Photonic Wire Bonding is a disruptive technology that was developed to enable optical connectivity for photonic circuits. Similar to traditional electronic wire bonding, which uses metal wires to connect circuits and enable data transfer with electrons, Photonic Wire Bonding uses optical wires to transfer data via light. By harnessing ultra-fast light pulses and the principle of two photon polymerization, the technology creates optical connections 50 times smaller than a human hair and invisible to the human eye. Photonic Wire Bonds act as a light bridge between key optical components and photonic circuits, allowing data to travel at the speed of light over short distances. Engineers envision these optical connections not only in data centers but also in personal devices and supercomputers, where faster, more energy-efficient data transmission will unlock significant advancements in technology.
Why Speed Matters
The potential of Photonic Wire Bonds lies in its ability to enable data transmission at unprecedented speeds. Current data transmission relies heavily on electrons traveling through metal wires, limited by resistance and thermal loss. As we generate ever-larger amounts of data, from HD streaming to massive AI computations, traditional electronic connections become bottlenecks, hindering speed and efficiency. Photonic Wire Bonding allows data to travel to where it is needed via photons, or particles of light, which experience little to no resistance. With light traveling five times around the Earth in one second, data can be transmitted almost instantly over short to medium distances, offering a pathway to ultra-high-speed, low-latency connections.
Applications and Future Impact
As more applications demand greater bandwidth, Photonic Wire Bonding shall transform data centers, cloud computing, and telecommunications. Imagine instant communication between servers in data centers, seamless real-time processing in AI systems, and smoother streaming experiences—all made possible by Photonic Wire Bonding. Additionally, because photonic systems generate less heat than traditional electronics, they are more energy-efficient, aligning with global commitments towards a sustainable future.
Challenges and Prospects
While the benefits of Photonic Wire Bonding are promising, challenges remain. Integrating this technology into existing infrastructure is complex and requires new materials and manufacturing processes. However, research in this field is advancing rapidly. As technology scales and costs decrease, we shall soon see Photonic Wire Bonding in everything from data centers to personal devices, heralding a new era of lightning-fast, energy-efficient data transmission.